LeetCode第138题—复制带随机指针的链表
今天获得了习近平七年知青岁月这本书,很开心!
自己代码的开源仓库:click here 欢迎Star和Fork :)
¶题目描述
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
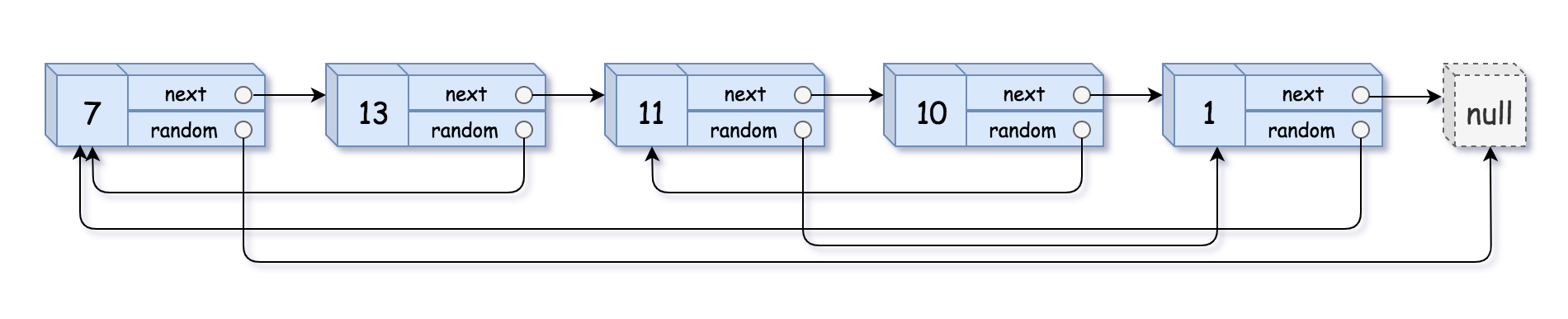
1 | 示例 1: |
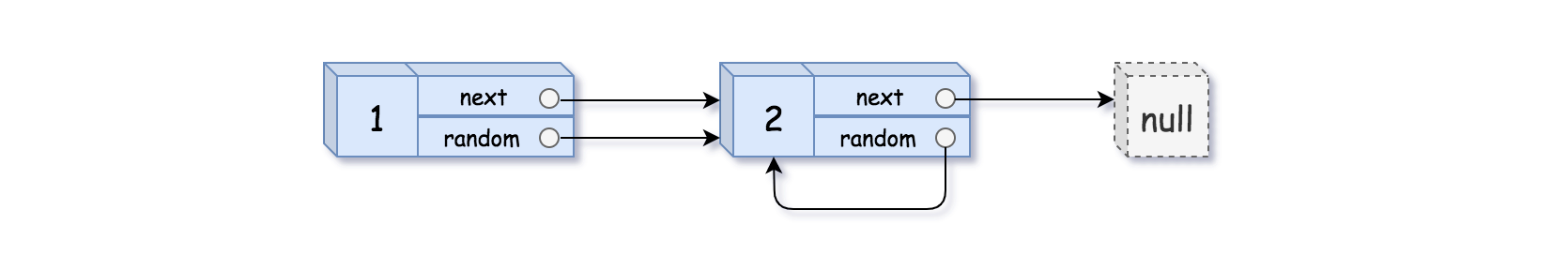
1 | 示例 2: |
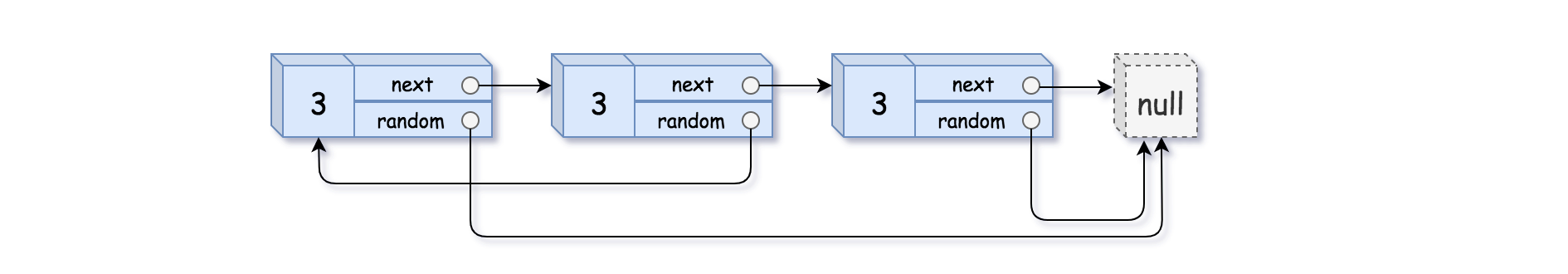
1 | 示例 3: |
¶代码
¶Python取巧方法(不建议!!!)
如果是生活中可以用库,真正OJ不建议使用。
1 | return copy.deepcopy(head) |
¶实打实的哈希方法
1 | class Node: |
